Introduction
What comes to mind when you think about Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR)?
- Ethical decision making
- Triple bottom line (People, Profit and Planet)(三重底线)
- Accountable Corporation
- Responsible business
- Good corporate citizen
- Good company
- Best business practice
What is leading me to this question is the idea that you know the corporate social responsibility can also mean it’s not just about charity. But if that idea of being a good company being a good citizen meant a company can be a citizen. So the same way we ask ourselves encourage each other to be good citizens. Corporations can also be encouraged to be good citizens.(公司也需要成为“好公民”)
What is CSR?
- CSR as ‘a concept whereby companies integrate social and environmental concerns in their business operations and in their interaction with their stakeholders(相关方) on a voluntary basis’ as they are increasingly aware that responsible behaviour leads to sustainable business success’
- (EU, 2003)(公司关注CSR,是在自愿的基础上进行的,而不是强制的,但这么做的目标是为了获得商业上的成功(所以这个定义很有趣))
- CSR as ‘… actions that appear to further some social good, beyond the interests of the firm and that which is required by law’
- (McWilliams & Siegel, 2001:117).(进一步促进社会利益)
- ‘…the CSR firm should strive to make a profit, obey the law, be ethical, and be a good corporate citizen’
- (Carroll, 1991:42).(需要注意Carroll’s CSR Pyramid和corporate citizen的概念,见后文)
- ‘Corporate social responsibility means something, but not always the same thing to everybody.To some it conveys the idea of legal responsibility or liability; to others, it means socially responsible behavior in the ethical sense; to still others, the meaning transmitted is that of ‘responsible for’in a casual mode; many simply equate it with the charitable contribution; some take it to mean socially conscious; many of those who embrace it most fervently see it as a mere synonym for legitimacy in the context of belonging or being proper or valid; few see a sort of fiduciary duty imposing higher standards of behavior on business-men than on citizens at large.
- ‘CSR is more about caring for any possible negative impact of business on society, avoiding harm to other people and the public at large, meeting increasing and changing social and stakeholder expectations, contributing resources to communities and helping improve the quality of life in society. ‘ (Sun, Steward and Pollard 2010)
Why CSR important?
- Business: key player in society
- Business a major change agent
- It has the potential to be a ‘force for good’or ‘for evil’
- Drives growth and prosperity
- Society: business does not operate in a vacuum
- Society impacts on business
- Society is constantly changing and so must business
Benefit of CSR
- Attract customers
- Reduce cost through efficiency
- Achieve advantage through innovation
- Improve reputation
- Attract the right people
- Minimise regulation
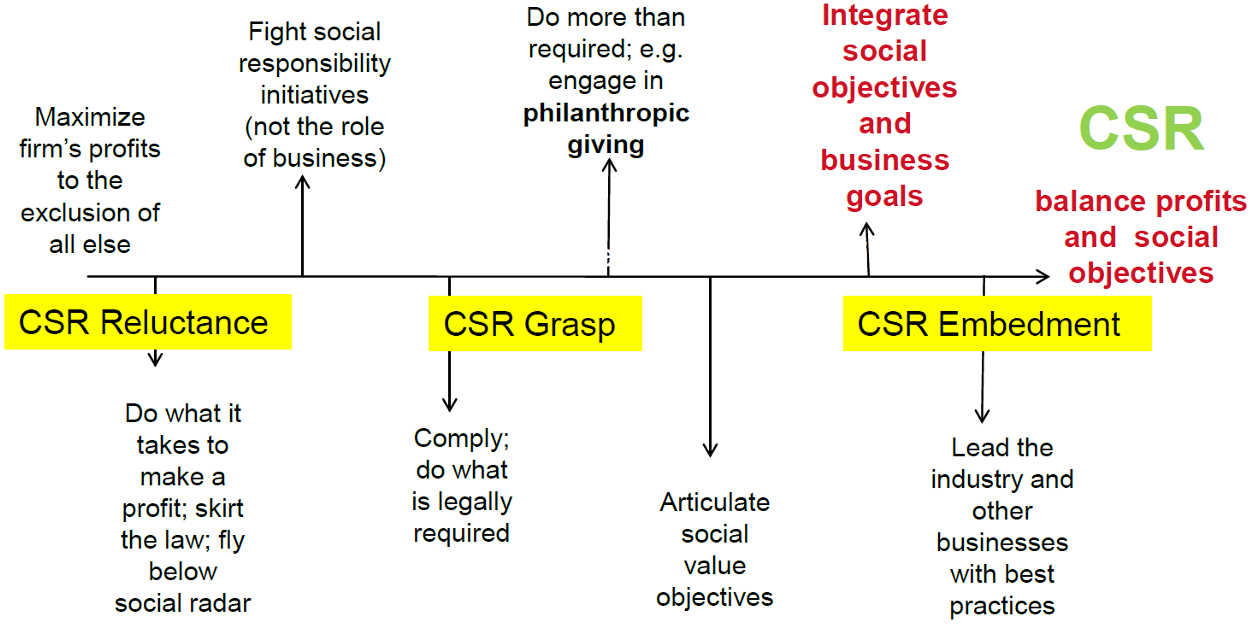
CSR theories and fundamental
Carroll’s CSR Pyramid(CSR金字塔)
- What is Carroll’s CSR Pyramid?
- Carroll’s pyramid of CSR.It is build on ideal and abstract business society with an implicit assumption that business do good and do no harm to society(假设企业做好事)

- From foundation to top (注意:这并不是优劣排序,不是说Economic就比Legal更重要,只是使用金字塔的形式进行梳理区分)
- Economic: For the business to survive on a long-term basis and benefit the society, the first responsibility of the company is to gain profits.(公司首要还是获取利润,不然就破产了)
- Legal: It is imperative for the company to obey and adhere to the laws and regulations related to the nature of its business, competition, employment, and health and safety among others.(遵守法律法规)
- Ethical: It is important for the company to act on the grounds of ethics and morals in society and should also go beyond the narrow requirements of the law and order.(单法律是最基本的,也总是落后的,除此之外,公司还需遵守伦理道德)
- Philanthropic: It is the responsibility of the company to give back to society. This facet of responsibility holds an important place even though it is discretionary in nature
- The pros of Carroll’s CSR Pyramid
- Easy to understand
- Suit for CSR concept and business (profit)
- The cons of Carroll’s CSR Pyramid
- May not suit for complex scenario
- Some arguments might put morals and ethics as foundation instead of profit generation.
CSR theories (Degree)
1、Instrumental theories
- Focus on achieving economic goals(专注于实现经济目标)
- To maximise shareholder value
- Strategies for achieving competitive advantages
- Cause related marketing
- Socially responsible firms receive more favourable recommendations.
2、Political theories
- Focus on the relationship between society and organisations and its responsibilities(关注社会和组织之间的关系及其责任)
- Corporate constitutionalism – business is a social institution and must use power responsibly
- Integrative social contract theory
- Corporate citizenship.
3、Integrative theories
- Looks at organisations response to social demands. The argument here is that business needs society for existence, continuity and growth.(探讨组织对社会需求的反应)
- Issues management – manage social issues
- The principle of public responsibility
- Stakeholder management – specific issues/stakeholder management
- Corporate social performance
4、Ethical theories
- These theories are based on the ethical contract between business and society.(企业和社会之间的道德契约)
- Universal rights – human rights, labour and environment
- Sustainable development
- The common good approach
How to evaluate CSR performance?
- Evaluating what they do and how well they do
- Evaluating what they fail to do
Corporate Citizenship
Reference
Abstract:We critically examine the content of contemporary understandings of corporate citizenship and locate them within the extant body of research dealing with business-society relations. Our main purpose is to realize a theoretically informed definition of corporate citizenship that is descriptively robust and conceptually distinct from existing concepts in the literature. Specifically, our extended perspective exposes the element of “citizenship” and conceptualizes corporate citizenship as the administration of a bundle of individual citizenship rights—social, civil, and political—conventionally granted and protected by governments.
Background
- Corporate Citizenship (CC) is poorly defined and used.
- Limited view (philanthropy, social investing,community relations, et cetera)(认为CC只是涵盖了CSR的一部分)
- Equivalent view (Corporate Social Responsibility)(认为CC和CSR是同等的概念)
- Problem: If CC is these existing concepts, why create a new concept?
- Solution: Extended view of Corporate Citizenship through Liberal Citizenship as the principal template for Western democracy(从 Corporate Citizenship–>Liberal Citizenship)(问题是:公司可以被视为公民吗?)
Liberal Citizenship
- Liberal Citizenship comprises three different aspects of entitlement: civil, social, and political rights (Marshall, 1965):
- Civil rights: freedom from abuses and interference by third parties – most notably governments – (e.g. right to free market)
- Social rights: freedom to participate in society (e.g. right to education)
- Political rights: active participation in society through politics (e.g. voting and holding political offices)
上述的自由公民权利通常由政府进行保障,因为政府有义务保障公民的权利。但是问题是,如果政府无法提供这种权利(Failure of nation state),应该怎么办?可能还有非政府组织(NGOs)的帮助。也可以让企业提供帮助,所以有了企业公民的加入,帮助满足公民权利。
Why Extended CC?
- Failure of nation state as the sole guarantor of citizenship rights has necessitated the intervention of business(企业帮助政府提供公民权利)
- partly because of globalisation which is a form of deterritorialisation of social, political, and economic interaction (Scholte,2000)
- “Corporations’”and“Citizenship’”come together in modern society at the point where the state ceases to be the only guarantor of citizenship (Matten and Crane,2005:171)
- so, Extended Corporate Citizenship is the role of the corporation in administering citizenship rights for citizens(在公民权利方面,公司能做的只是成为一个推动者,并没有从政府手中接过这一职责,只是帮助或者影响政府,使政府能够发挥其作用)

Corporations and citizenship
- Ref:Crane A, Matten D, Moon J. Corporations and citizenship: Business, responsibility and society[M]. Cambridge University Press, 2008.(这本书对CC和政府的关系做了进一步论述)
- 1、Corporations as citizens
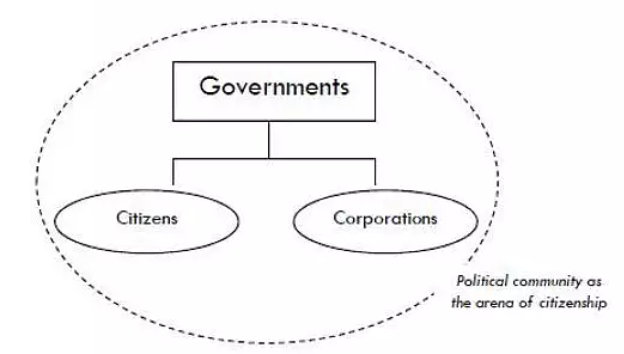
- 2、Corporations as governments
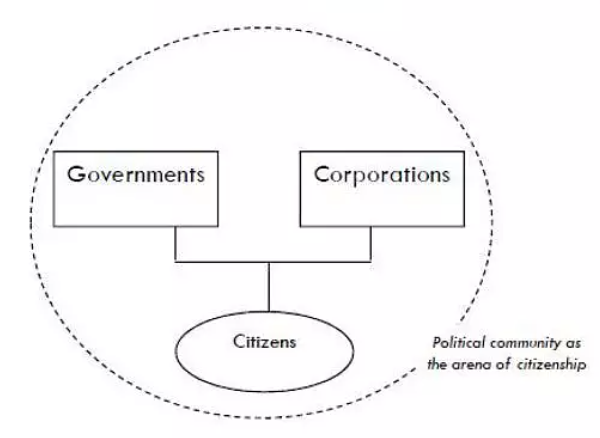
- 3、Stakeholders as citizens
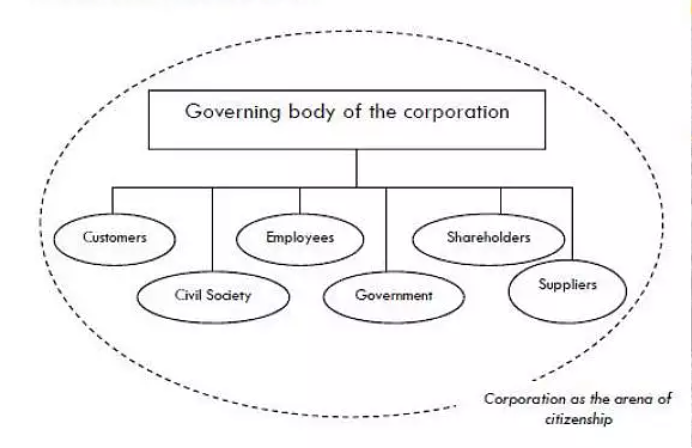
- 可以看到,企业将变得如此之大,甚至政府服从于企业(数字科技公司,e.g.Facebook),因此企业正成为政府。如果将这种关系放到全球化的背景下进行观察呢?
Political CSR
Reference
Abstract: Scholars in management and economics widely share the assumption that business firms focus on profits only, while it is the task of the state system to provide public goods. In this view business firms are conceived of as economic actors, and governments and their state agencies are considered the only political actors. We suggest that, under the conditions of globalization, the strict division of labour between private business and nation-state governance does not hold any more. Many business firms have started to assume social and political responsibilities that go beyond legal requirements and fill the regulatory vacuum in global governance. Our review of the literature shows that there are a growing number of publications from various disciplines that propose a politicized concept of corporate social responsibility. We consider the implications of this new perspective for theorizing about the business firm, governance, and democracy.
- 商业将成为在全球化背景下的政治新角色。政治企业社会责任提出了一种与商业公司合作的扩展治理模式,有助于全球监管以及提供公共产品。这也再次预示着中国企业将走向海外。
- So, in this case, it goes beyond the instrumental view of politics in order to develop a new understanding of global politics. We have private actors such as corporations and civil society organizations play an active role. In the Democratic regulation and control of market transactions, so that’s the whole thing about political seers are moving away from the nation state to think about the role of business in a globalized world.
CSR as Governance of Externalities
Reference
Abstract: We propose that corporations should be subject to a legal obligation to identify and internalise their social costs or negative externalities. Our proposal reframes corporate social responsibility (CSR) as obligated internalisation of social costs, and relies on reflexive governance through mandated hybrid fora. We argue that our approach advances theory, as well as practice and policy, by building on and going beyond prior attempts to address social costs, such as prescriptive government regulation, Coasian bargaining and political CSR.(CSR是关于外部性的治理)
externalities/impacts
Costs or benefits of production or consumption experienced by society but not by the producers or consumers themselves. Sometimes referred to as ‘spillover’ or ‘third-party’ costs or benefits (Sloman,2000).