The purpose of this module is to explore the theoretical underpinnings of the SDGs and to further explore relevant business and social enterprise development in their context.
We had done today for present an overview of the multinational firms while they are and how their challenges the pros and cons as well as how they are implicated in the globalization process.
Fundamental Knowledge
What is business
- The term business refers to an organisation or enterprising entity engaged In commercial, industrial, or professional activities.
- Business generally refers to organisations that seek profits by providing goods or service in exchange for payment.
- But there is also could be non-profit organisations that operate to fulfill charitable mission or social cause.
- Non-profit organisations may not be the majority of business, so in the following content we only discuss for-profit business.
Two majority components of trading process.
- Customer:
- They would like to purchase something for their needs, such as hungry and happiness.
- The cost for customer is money.
- Business/Company:
- They would offer product or service to fulfill consumer needs.
- The revenue is money.
- A simple business process

Ownership type
- Private Company
- Sole Trading Enterprises
- Partnership Enterprises
- Public Company(上市公司)
- Limited Liability or Unlimited Liability
- Private Limited Liability Company – Pty. Ltd.
- Public Limited Liability Company – Ltd.
- Corporation:
- A group of people acts together as a single entity.
- Owners are commonly referred to as shareholders.
- Shares:
- A share is an indivisible unit of capital, expressing the ownership relationship between the company and the shareholder.
- If there is no other conditions, more than half of shares could have authority to control or make decision for the company.
- Parent company and subsidiary company(母公司和子公司)
- A business enterprise can establish smaller, separate entities called subsidiary companys
- The subsidiary could focus on a specific area of the business such as a product line.
- As the parent company are the majority that owns most subsidiary company’s shares, parent company control over the subsidiary company.
- Joint Venture:(合资企业)
- A joint venture is similar to a partnership.
- Two or more companies form a single joint venture company.
- These companies entre a contractual agreement and invest funds to form the business.
- Each joint venture owners share the interests and management responsibilities.
Precondition of Commerce and Economics
- There are three important preconditions for pricing and economics:
- People are rational (for both customer and enterprise)
- People respond to economic incentives (seek for benefits or profit, not loss)
- Optional decision are made at the margin (seek more)
Business Environment– PEST(LE) analysis
- Political
- Economical
- Social-cultural
- Technological
- (Legal)
- (Environmental)
- These six elements could directly influence business operation as external business environment.
- If the business has low influence level with host countries, it is hardly to influence the local condition. And the company have to seriously consider how to survive in such business environment.
- But what if the business is strong enough, such as Apple, Google, and Boeing. They have such influence and fund to influence the host country, what could happen with local country with above elements?
What is a Global Business?
Multinational Enterprises
What is Multinational Enterprises (MNEs/MNCs)?
- “An enterprise that owns or controls production or service facilities outside the country in which they are based. ” (United Nations 1973-Multinational Corporation in World Development)
- “A firm that controls and manages plants located in at least two countries. ” (Cave R.1982-Multinational Enterprise and Economic Analysis)
- “A firm that engages in foreign direct investment and owns and controls value adding activities in more than one country. ” (Dunning, J. H,1993-Multinational Enterprise and Global Economy)
so over that period between 1973 and 1993, 20 years you see that there were kind of different definitions, but all converging or certain characteristics which would include ownership, control , number of locations at least as well as the activities whether you’re looking at foreign direct investment or production or service facilities.(MNEs更像是母公司和子公司的控制方式)
Multinational Global & Corporation
- Multinational Corporation : A collection of relatively independent subsidiaries, each focused on a specific local market. A decentralised unit free to customise its products/services,focus its marketing, select and recruit its personnel to meet the needs of its customers.(不同的地区根据当地的特色有不同的产品)
- Global Corporation: Here, the whole world is seen as its market place, with goods and services standardised to meet the needs of the customers worldwide. Power and authority will be concentrated in the corporate headquarters.(产品的基本属性全球市场基本是统一的,比如苹果手机)
Transnational Corporation (TNC)
What is Transnational Corporation?
- Transnational Corporation [TNC]: “an enterprise that controls assets of other entities in countries other than its home country, usually by owning a certain equity capital stake An equity capital stake of 10% or more of the ordinary shares or voting power for an incorporated enterprise, or its equivalent for an unincorporated enterprise, is normally considered the threshold for the control of assets. “
- Transnational Corporation [TNC]: “a firm that has the power to coordinate and control operations in more than one country, even if it does not own them” (Dicken,2007:16) (TNCs更像是合资公司,记住至少要10%的控制权。因为可以根据当地的情况进行调整。)
TNCs three characteristics
- Ability to coordinate and control: processes and transactions within Trans-National Production Networks (TNPs)
- Potential ability to take advantage of geographical differences in
- the distribution of the factors of production (e.g. natural resources, capital, labour)
- state policies (e.g. Taxes, trade barriers, subsidies etc)
- Potential geographical flexibility : ability to switch location of resources-operations (Dicken 2007, p106)
Operating Characteristics
- Can reduce their sourcing and distribution costs
- Can avoid tariffs, quotas and other trade barriers faced by exporters.
- Are able periodically to shift operations from high cost to low cost countries.
- Can penetrate markets throughout the world from supply points in several different countries.
- MNC managements plan, organise and control — operations on a worldwide scale, with national markets being regarded as little more than segments of a broader regional customer base.
- Internal integration at the multinational level creates many possibilities for economies of scale and the spreading of costs over multiple markets.
- A number of top jobs in an MNC will usually be allocated to the nationals of various foreign
countries
- There will be joint strategic decision making by headquarters and managers of foreign subsidiary units.
- Technologies are developed in which ever countries have the necessary skills, research infrastructures and facilities.
- Technology transfer benefits the host country through introducing fresh ideas and practices and by improving the research and development infrastructure of the nation.
- Latest management techniques and business methods are too diffused internationally.
Personal Insight
Why are companies, especially TNC/MNCs crucial for achieving the SDGs?
- The financial power, number of employees, expertise, global supply chains, global internal policies and Corporate Social Responsibility actions of multinational companies make them important partners in achieving the SDGs.
- TNC is a decentralized structure that operates or facilitates the production of goods and services in more than one country and not in its home country.
- MNC is a centralized management structure that runs its production of investment, services, or management at least in one country along with its home country.
- TNC and MNC are similar meanings with minutiae differences in their operations of production of goods and services.
| TNC | MNC | |
|---|---|---|
| Meaning | Transnational Corporation is a decentralised enterprise that subsumes its production of goods and services, Fx or any investments with more than one country. TNC set its network in developing countries for cheap cost of production. | Multinational Corporations is a centralised company that runs the production of goods, services, investment and management in its home country as well as in other countries. |
| Headquarters | TNC Headquarters doesn’t locate in its home country but in some other developing country where production occurs. | MNC main Headquarters located in its home country– where the production of goods began initially. |
| Structure | Transnational corporation follows decentralised structure- the corporation operates in numerous countries where goods and services are produced. | Multinational Corporation is a centralised management structure, where the home country is considered the main headquarters- while operating other countries for production. |
| Examples | A renowned company Nestle is a Transnational company that runs its operations in more than one developing countries. | Microsoft. Coco-Cola, IBM and Apple etc. are the renowned Multinational companies in the world. |
Criticisms of MNCs
- So based on this characteristics of MNCs so have people who advocate for more nationals and so they saw the arguments. (跨国公司对宿主公司的好处和坏处)

- So what are the positive/negativity things global businesses can offer?

Criticisms: Political
- Supporting repressive governments
- Paying bribes to secure political influence
- Paying protection money to ‘dodgy’groups
- Destabilising national governments
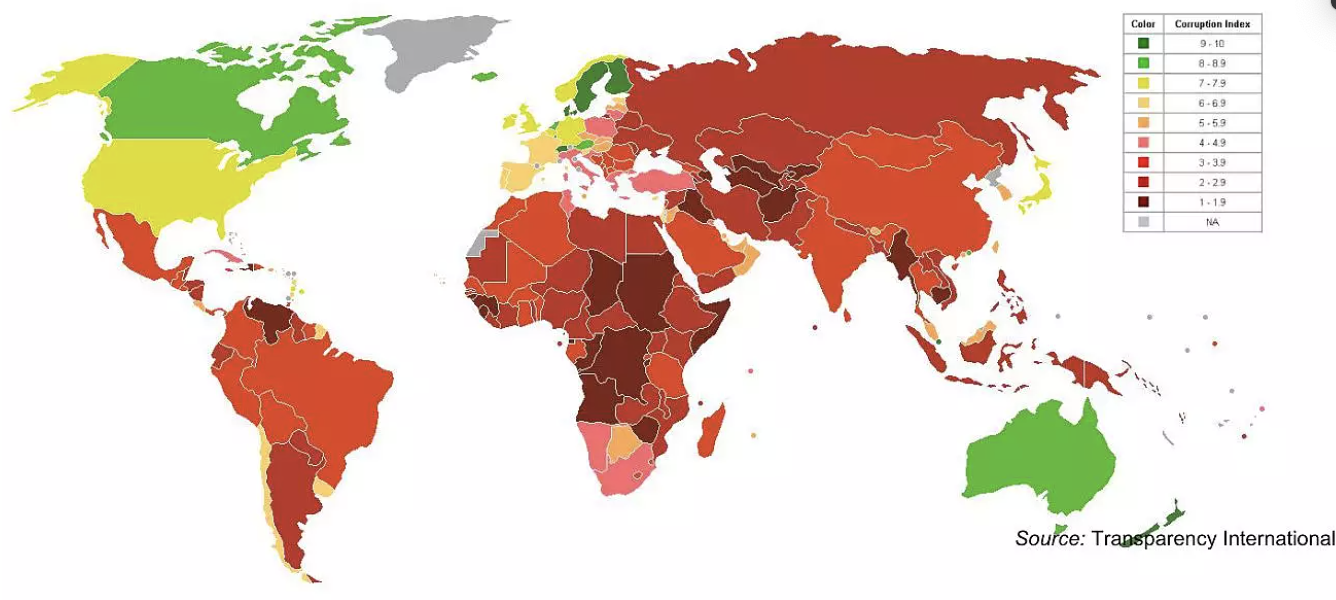
- Data Case: Transparency International Corruption Perception Index (CPI)
- This map is based on the latest Transparency International Corruption Perception Index (CPI). The CPI Score relates to perceptions of the degree of corruption as seen by business people, academics and risk analysts, and ranges between 10 (highly clean) and 0 (highly corrupt).
Criticisms: Sales and marketing
- Undermined ancient cultures and traditions through the use of advertising and marketing methods.
- Supplied products that are inappropriate to local needs.
- Not accepted responsibility for unsafe products.
- Promoted goods that waste valuable resources in developing countries
Criticisms: Environmental management
- Depleting natural resources too quickly
- Polluting the environment (FDI-Pollution Granger causality analysis)
- Causing harmful changes in local living conditions
Criticisms: Technological
- Using technologies that are inappropriate for the needs of local economies
- Encouraging ‘brain drain’ from developing countries.
- Making host countries technologically dependent on MNC’s home countries.
- Not training nationals in the operation of imported technologies (for ethnocentric MNCs)
Criticisms: Economic
- Sometimes import raw materials from abroad rather than procure them locally
- Repatriation of profits thus straining the host country’s balance of payments
- Dominate technology advanced sectors of the economy (the infantry industry argument)
Conflicts with Host Countries and their control techniques
**Two main conflict areas **
- MNC control and utilisation of host country resources.
- Disagreements about the division of profits from local operations.
- may attempt to use lowest cost areas in the most productive manner, but
- local governments have expectations of higher levels of employment
Techniques of Host Country Controls
- Special taxes
- Minimum wage requirements
- Exchange controls, and
- Regulations requiring that:
- A certain number of host country nationals be employed at managerial levels.
- A subsidiary’s export value attain a specific annual value.
- Imports be restricted
- Very latest technology be used in production
- Obtain import/export licenses
- Having local joint venture partners
- As an MNC’s assets are usually located in its home country:
- The home country government can adopt a threatening posture towards these assets.
- Senior executives as citizens of the home country are subject to the laws and regulations of the home country.
- MNC executives and home country shareholders will probably support home country’s basic economic objectives.
Globalisation
Global businesses are implicated in globalisation and its processes
What is globalization?
- “a process, which embodies a transformation in the spatial organization of social relations and transactions.. Generating transcontinental or interregional flows and networks of activity (Held et al.,1999:16)
- “…the extent to which the economic, political, cultural, social, and other relevant systems of nations are actually integrated into World Systems” (Clark and Knowles,2003:368)
- “..part of a powerful political-economic ideology through which capital-labour relationships and relative class power positions are shifted in profound ways” (Swyngedouw,2004:28)
Globalisation -A Political, Social and Economic Phenomenon

Consequences and Challenges of Globalisation Global Governance Gaps